Eyelid – a thin fold of skin that covers and protects the eye from dust and foreign bodies
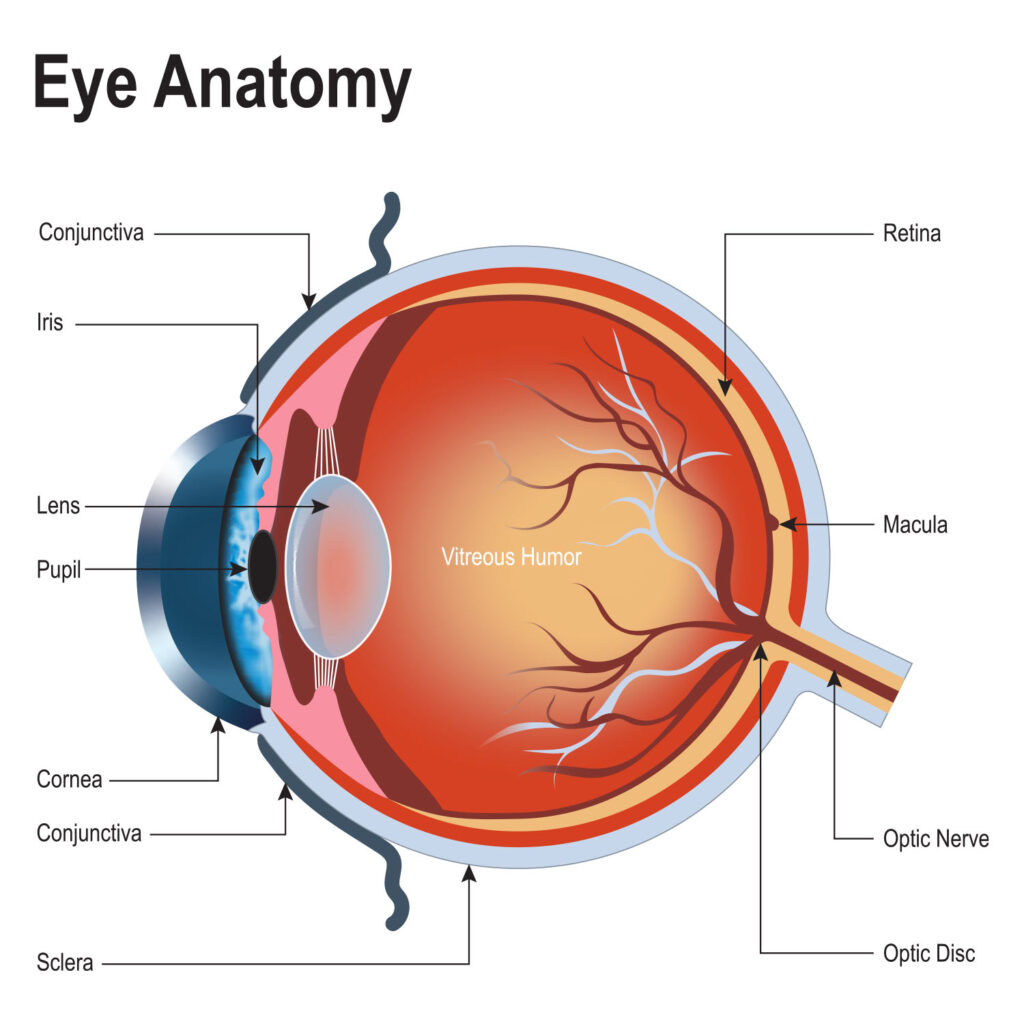
Conjunctiva – tissue that lines the inside of the eyelid
Tear film – a thin fluid layer over the outer surface of the eye
Sclera – the white of the eye
Cornea – the clear, transparent structure at the front of the eye that transmits and focuses light into the eye
Iris – the coloured part of the eye that regulates the amount of light that enters
Pupil – the dark centre in the middle of the eye
Lens – a transparent structure inside the eye that focuses light on the retina
Vitreous humor – a jelly-like substance that fills approximately 65% of the space within the eye
Retina – the nerve layer that lines the back of the eye; it senses light and creates electrical impulses that travel through the optic nerve to the brain
Macula – the small area of the retina with the fovea in the centre that contains special light-sensitive cells and allows you to see fine details clearly
Optic nerve – connects the eye to the brain and carries electrical impulses from the retina to the visual cortex of the brain